How Does Blockchain Work?
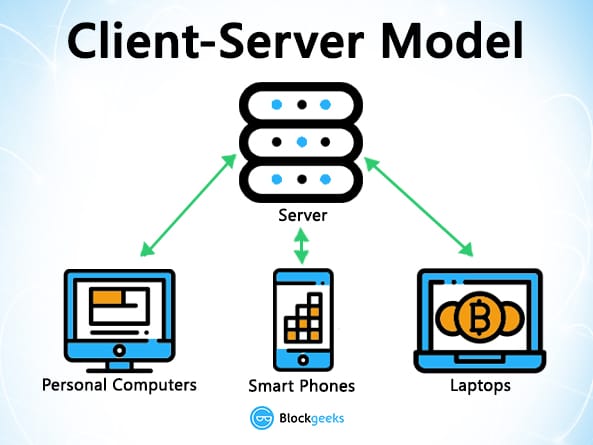
When you google search for something, you send a query to the server who then gets back at you with the relevant information. That is simple client-server.
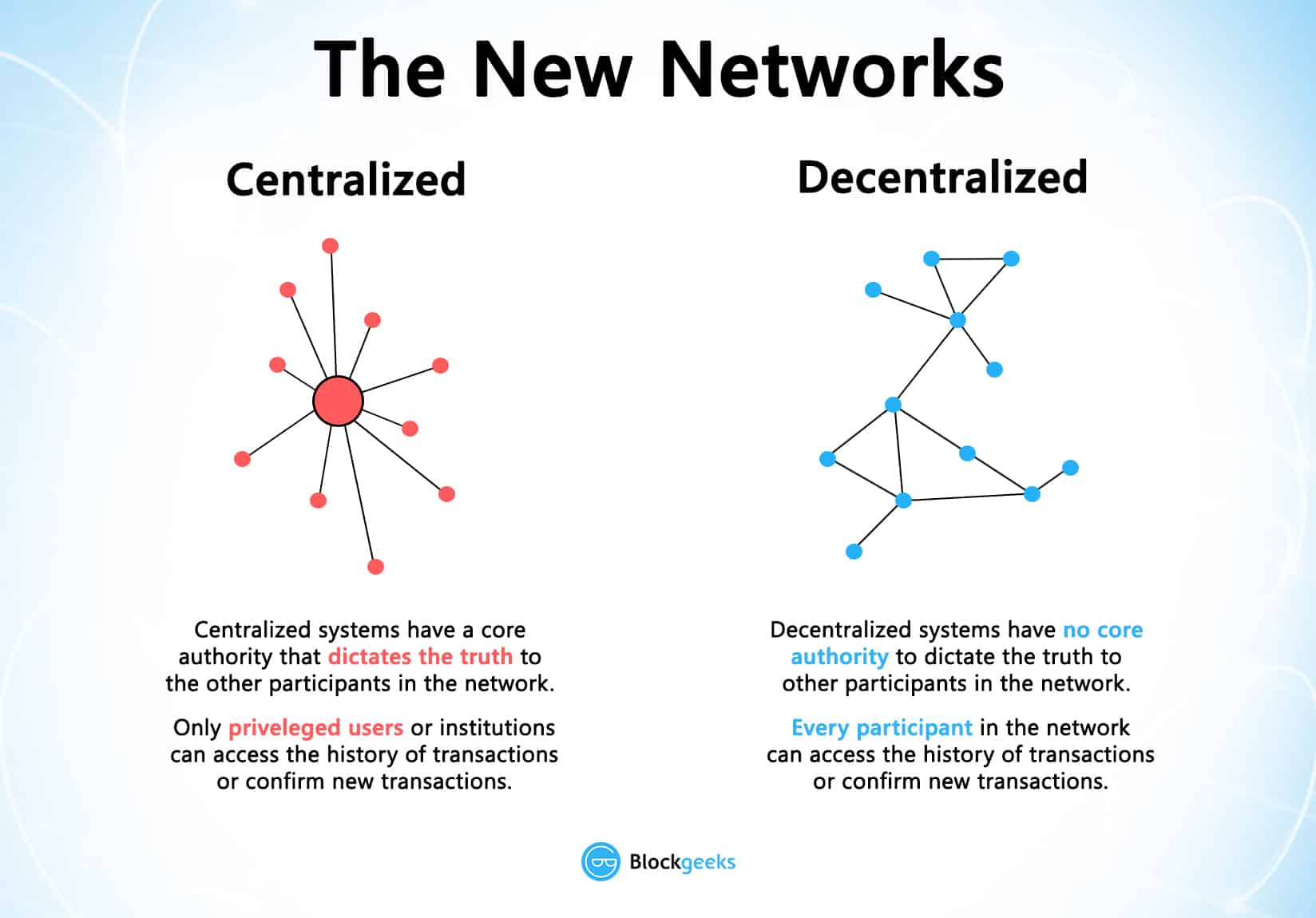
Now, centralized systems have treated us well for many years, however, they have several vulnerabilities.
- Firstly, because they are centralized, all the data is stored in one spot. This makes them easy target spots for potential hackers.
- If the centralized system were to go through a software upgrade, it would halt the entire system
- What if the centralized entity somehow shut down for whatever reason? That way nobody will be able to access the information that it possesses
- Worst case scenario, what if this entity gets corrupted and malicious? If that happens then all the data that is inside the blockchain will be compromised.
So, what happens if we just take this centralized entity away?
In a decentralized system, the information is not stored by one single entity. In fact, everyone in the network owns the information.
In a decentralized network, if you wanted to interact with your friend then you can do so directly without going through a third party. That was the main ideology behind Bitcoins. You and only you alone are in charge of your money. You can send your money to anyone you want without having to go through a bank.

Pillar #2: Transparency
One of the most interesting and misunderstood concepts in blockchain technology is “transparency.” Some people say that blockchain gives you privacy while some say that it is transparent. Why do you think that happens?
Well… a person’s identity is hidden via complex cryptography and represented only by their public address. So, if you were to look up a person’s transaction history, you will not see “Bob sent 1 BTC” instead you will see “1MF1bhsFLkBzzz9vpFYEmvwT2TbyCt7NZJ sent 1 BTC”.
The following snapshot of Ethereum transactions will show you what we mean:

nice
ReplyDeleteGOODDDD
ReplyDeleteNICE
ReplyDeletegood one
ReplyDeletegood
ReplyDelete